“`html
Top 7 Effective Solutions for an Animal-Based Diet in 2025: Discover the Benefits & Tips
An animal-based diet is gaining traction as a powerful approach to nutrition that focuses on the consumption of animal-derived foods. With numerous benefits including enhanced nutrient density, muscle recovery, and weight management, understanding the effective ways to implement this diet can be essential. This article delves into the advantages of an animal-based diet, providing practical tips for incorporating high-protein meals and diverse animal protein sources into your routine.
Understanding the Benefits of an Animal-Based Diet
The **benefits of an animal-based diet** are extensive. One of the primary advantages is the concentration of essential nutrients such as vitamins and minerals present in animal foods. Nutrient-rich animal foods like grass-fed beef, pasture-raised chicken, and seafood offer high bioavailability of nutrients, which means your body can absorb them more efficiently compared to plant sources. For instance, omega-3 fatty acids from fish are crucial for brain health and reducing inflammation, making them indispensable in any balanced diet.
The Nutritional Edge of Animal Protein Sources
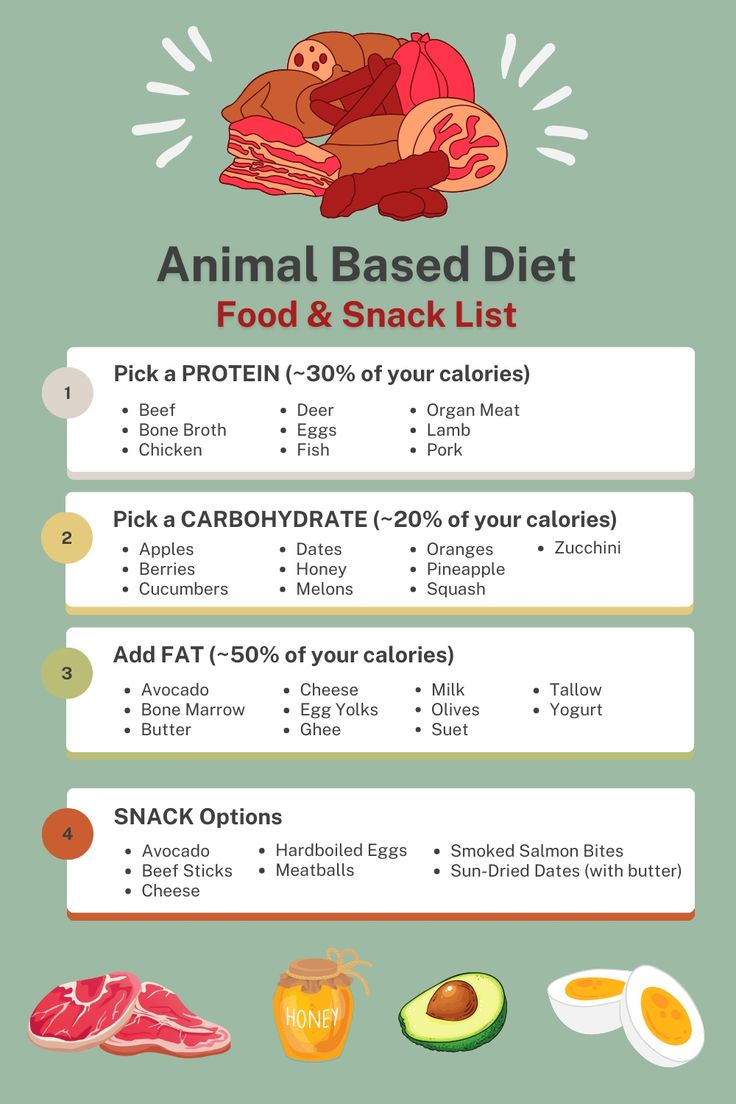
When discussing **animal protein sources**, it is vital to highlight their role in various diets such as the **keto animal-based diet** and the **paleo animal-based diet**. Each of these diets emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods that not only satiate hunger but provide substantial energy. Meats, dairy, and particularly organ meats like liver are rich in micronutrients that support overall health. For a varied approach, consider including eggs as a **complete protein**, offering a significant protein intake for athletes and active individuals looking to optimize muscle recovery.
Digging Into Digestive Benefits
Another remarkable benefit of an animal-based diet is its potential for improving gut health. **Digestive benefits of animal protein** include the presence of specific enzymes and probiotics found in fermented dairy products that help maintain a balanced microbiome. Additionally, the breakdown of animal fats in the diet is essential for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, further enhancing overall nutrient utilization. As modern diets trend toward high-carb consumption, reintroducing animal products could help rebalance digestive health.
Environmental Impact and Ethical Consumption
In the discussion surrounding an animal-based diet, it is crucial to address perceptions related to its **environmental impact**. Supporting **sustainable animal farming** practices and sourcing meat ethically can vastly minimize negative effects on the planet. Choosing local meat suppliers and prioritizing **grass-fed vs grain-fed meat** allows consumers to be part of a responsible food system, reflecting a commitment to environmental stewardship while still reaping the health benefits associated with animal products.
Practical Tips for Transitioning to an Animal-Based Diet
Switching to an animal-based diet may seem daunting, but implementing some practical steps can make it manageable. Meal planning is essential for creating a balanced diet that prioritizes **high-protein meals** while incorporating variety in animal products.
Creating Balanced Animal-Based Meals
When preparing **animal-based meals**, focus on incorporating a variety of protein sources and healthy fats from animals. For example, a staple meal could include grilled grass-fed steak with avocado and sautéed leafy greens in a cooking fat like ghee or tallow. This not only provides energy but enhances nutrient variety with each meal. Moreover, think about meal timing for athletes to ensure your body is primed for performance and recovery post-exercise. A post-workout meal rich in animal protein can enhance muscle recovery and promote hormone balance.
Selecting Quality Meat
**Quality meat selection** is critical to a successful animal-based dietary transition. Choosing organic or sustainably raised meats often means fewer hormones and antibiotics in your food, which can positively affect health. Additionally, consuming organ meats and various cuts of meat can not only add flavors to your dishes but also provide a broader spectrum of nutrients necessary for optimal health. Don’t hesitate to explore different cooking techniques from grilling to slow cooking to find what best suits your palate.
Incorporating Delicious Animal-Based Snacks
Don’t overlook **animal-based snacks** as part of your dietary routine. Options such as beef jerky, hard-boiled eggs, and cheese can satisfy cravings without resorting to overly processed foods. Planning your snacks around animal products can ensure that you maintain your protein intake throughout the day, keeping your energy levels stable. Remember that hydration plays a role in fermentation and flavor profiles; ensure you are drinking enough fluids while enjoying these nutritious snacks.
Examining the Role of Dairy in an Animal-Based Diet
Dairy can play a significant role in an effective animal-based diet, especially when seeking sources of calcium and beneficial bacteria. However, it’s essential to understand the different types of dairy and their benefits. The choice between dairy alternatives and regular dairy products can be guided by personal preference and digestive tolerance.
The Nutritional Benefits of Dairy in the Diet
Dairy products are known for their dense nutrient profile, including important vitamins such as Vitamin D and calcium. **Raw milk benefits** are often highlighted for their probiotics and superior flavor. Incorporating cheese and yogurt into your diet can provide not just protein but also enrichment for gut health. Look for sources that prioritize animal welfare and sustainable practices for an ethical addition to your meal plan.
Exploring Dairy Alternatives
For those who don’t tolerate dairy well, exploring **dairy alternatives** made from coconuts, almonds, or soy may provide some solutions, although it’s crucial to ensure these alternatives aren’t heavily processed or fortified with additives. Alternatively, choosing lactose-free options might retain many beneficial properties of traditional dairy without triggering adverse reactions. Fostering a keen understanding of personal dietary needs is imperative in optimizing your approach to animal-derived foods.
Key Takeaways
- The diversity and nutrient density of animal products provide extensive health benefits.
- Ethical sourcing and understanding the environmental impact of your food choices are crucial.
- Quality meat selection, including organ meats, enhances nutritional balance.
- Incorporating dairy can provide vital nutrients if tolerated; otherwise, opt for suitable alternatives.
FAQ
1. What are the environmental impacts of an animal-based diet?
The environmental impacts can vary widely based on sourcing and farming practices. Sustainable animal farming and local sourcing reduce the negative effects of carbon emissions typical of industrial agriculture.
2. How can I ensure my protein intake is adequate on an animal-based diet?
Focus on incorporating various high-protein animal products such as meats, eggs, and dairy. Utilizing meal prep can also help you track intake and stay consistent. For athletes, protein timing is also essential for performance and muscle recovery.
3. Are there specific animal foods that are better for gut health?
Yes, incorporating fermented dairy products like yogurt and kefir can be beneficial for gut health. Additionally, nutrient-rich options like organ meats can enhance digestive health due to their high enzyme content.
4. How do I start transitioning to an animal-based diet?
Begin by gradually replacing processed foods with whole animal products. Focus on meal prep and include a variety of foods such as red meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy, tailoring the plan to fit your lifestyle and dietary preferences.
5. What role can cooking methods play in an animal-based diet?
Cooking methods can enhance flavor and nutrient availability; techniques such as slow cooking, grilling, and simmering can offer rich tastes and are essential for making the most out of every animal product consumed.
“`